
Many people often wonder about the best image file format in AVIF vs WebP. This leads to confusion between AVIF and WebP image file formats.
Which one is best in AVIF and WebP?
Which one should we use?
AVIF and WebP are modern image file formats designed to offer better compression and quality than older formats like JPEG and PNG.
Let’s discuss this in detail…
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the WebP File Format?
WebP is a modern image format designed to make web pages load faster.
It gives high-quality images in smaller sizes than JPEG.
WebP is an image format developed by Google designed to offer efficient compression and high-quality image decoding.
It is particularly well-suited for web images, offering smaller file sizes without compromising visual quality.
It was designed as a modern alternative to traditional image formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF.
WebP supports both lossy and lossless compression, so you don’t have to sacrifice image quality while reducing its file size.
This makes it especially useful for web pages and other applications where image loading speed is essential.
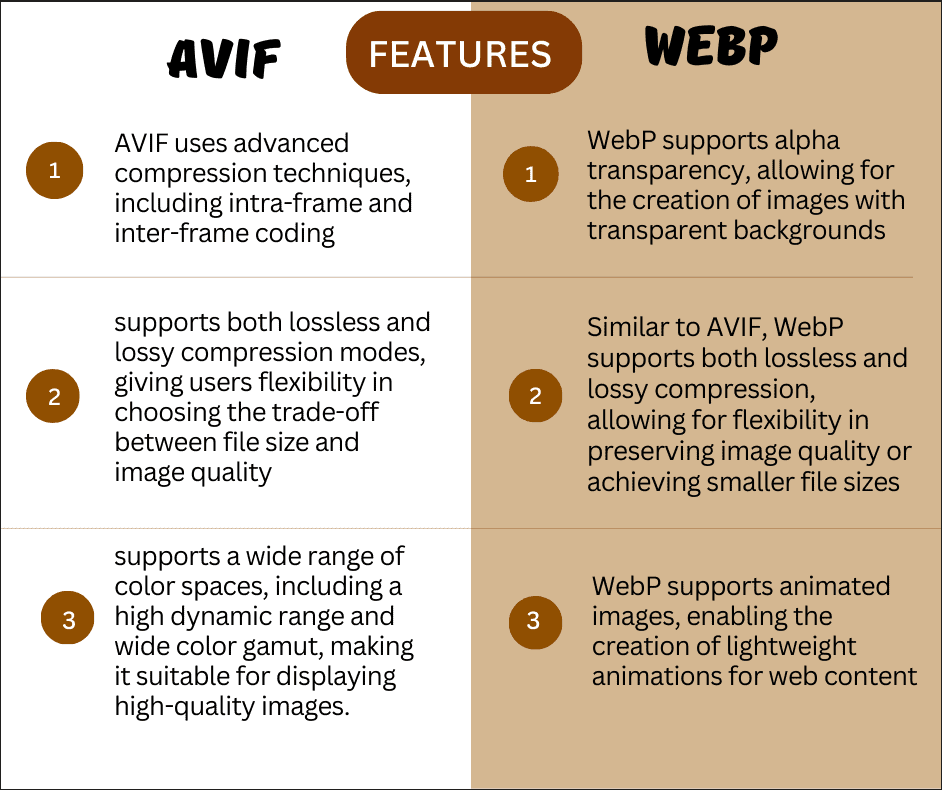
Moreover, Webp supports animation and alpha transparency; it can display animations with smaller file sizes.
Alpha transparency allows images with transparent backgrounds to blend seamlessly with different web page elements.
What is the AVIF File Format?
The AVIF file format, which stands for AV1 Image File Format, is an open and license-free image file format.
AV1 Image file is an open and license-free image file format for storing images compressed with AV1 in HEIF (High-Efficiency Image File Format)
Developed by the Alliance for Open Media, it stores images or image sequences compressed with AV1.
AVIF was designed as an alternative to other image formats such as JPEG, PNG, and WEBP.
It offers better image quality and smaller file sizes than JPEG, making it an attractive option for web and mobile applications.
You can compress video with high efficiency with the help of AV1 compression.
The AVIF file format has gained popularity due to its superior compression capabilities and improved image quality.
However, it’s worth noting that AVIF is still not widely supported across all platforms and applications.
Support for AVIF files may vary depending on the operating system, web browser, and image editing software.
When Should you use WebP and AVIF file formats?
There are some considerations when deciding which format to use in specific situations.
When to Use WebP?
If Browser Compatibility is Required:
WebP is widely supported by popular web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. WebP is compatible with a wide range of browsers.
If You are Using Animation:
WebP supports static and animated images, making it suitable to use animation on your website.
Lossless Compression:
WebP offers lossless compression, which means you can achieve smaller file sizes without sacrificing image quality.
This can be beneficial for applications that require high image quality.
When to Use AVIF:
Higher Compression Efficiency:
AVIF has higher compression efficiency than WebP and even older formats like JPEG.
It can achieve file sizes that are around 50% smaller than JPEG.
Image Quality:
AVIF supports 10- and 12-bit colors, making it ideal for applications that require high-quality images with a wide color range.
It also supports HDR (High Dynamic Range) and color profiles. It helps in providing rich color images.
Future Compatibility:
AVIF is gaining momentum and is supported by major tech companies like Google, Microsoft, and Mozilla.
Using WebP File Format Benefits
Here are some of the best uses of the WebP file format:
Faster Web Page Loading:
WebP files tend to be smaller than their JPG and PNG, resulting in faster page loading.
Improved Website Performance:
WebP files can improve websites’ overall loading and performance, even when you have image files.
Smaller file sizes:
WebP files are up to 34% smaller than comparable JPG files at the same SSIM quality index.
This translates to faster image loading times, even with low bandwidth.
Animation Capabilities:
The WebP format can present animations, much like GIFs, and offers several advantages.
Using AVIF File Format Benefits
The best uses for AVIF file format include:
Web Usage:
AVIF is highly recommended for web usage as it can significantly reduce file sizes without compromising image quality.
High-Quality Images:
AVIF can be saved in still and animation format and supports multiple color spaces.
It allows for storing high-quality images with smaller file sizes, making it suitable for digital design and other applications where image quality is dominant.
Lossless and Lossy Compression:
It supports both lossless and lossy compression. This flexibility allows for greater control over the trade-off between image quality and file size, making AVIF ideal for various use cases.
To open AVIF files, you can use web browsers like Chrome (v85 or later) or Firefox (v93 or later), the GIMP image editor.
AVIF vs. WebP
Compression and File Size:
AVIF and WebP are designed to provide improved compression and smaller file sizes than traditional formats like JPEG.
However, AVIF offers better compression than WebP, even in smaller file sizes.
Features and Capabilities:
AVIF supports lossy and lossless compression, transparency, and animation. It can handle 10- and 12-bit colors at a full resolution.
On the other hand, WebP also supports lossy and lossless compression, transparency (alpha channel), and animation (GIF replacement).
However, AVIF tends to have better quality and compression-to-appeal ratio, especially for high-appeal photos.
Browser Support:
WebP has better browser support than AVIF—popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge support WebP.
In contrast, AVIF is only supported by some browsers and requires additional JavaScript.
Image quality:
AVIF and WebP use advanced compression algorithms, such as a combination of lossy and lossless techniques, to preserve image details while reducing file size.
The visual quality of images can vary depending on the settings used during compression.
Encoding and Decoding time:
AVIF generally requires more time for encoding and decoding than WebP.
This is because AVIF uses more complex compression techniques, which can lead to longer processing times.
Color Gamut and HDR:
AVIF supports a wide range of color spaces, including HDR and a wide color gamut, which allows it to produce high-quality images.
On the other hand, WebP has limitations in this aspect, supporting a maximum bit depth of 8-bit. Regarding color gamut and HDR support,
AVIF appears to offer more advanced capabilities than WebP.
How to Choose Between AVIF and WebP
When choosing between AVIF and WebP, you may want to consider the following factors:
Browser Support:
WebP is supported by the most popular browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. AVIF, on the other hand, is only supported by some of the newer versions of these browsers.
You may want to stick with WebP for now to ensure maximum compatibility.
File Size:
Both AVIF and WebP offer significant reductions in file size compared to traditional image formats like JPEG and PNG.
However, in some cases, one may perform better than the other.
It’s worth testing both formats on your specific images to see which one results in the best file size reduction.
Quality:
Both formats offer high-quality image compression, but the results may differ depending on the image.
It’s worth testing both formats on your images to see which produces the best quality.
Workflow:
AVIF and WebP have their own encoding and decoding workflows, which may require different software and tools.
Ensure you have the tools and knowledge to work with your chosen format.
What do You do if You have JPEG & PNG Images?
If your website currently uses jpeg & png images and you are considering transitioning to a more modern and efficient format, such as AVIF or WebP, here are some steps to consider:
Evaluate Your Image Usage:
Inventory all the JPEG/PNG images used on your website.
Identify the images that are frequently accessed and are impacting page load times.
Convert to WebP:
For a seamless transition, consider converting your JPEG images to WebP format.
There are various tools and libraries available that can automate the conversion process, ensuring that your images are optimized for WebP compatibility.
Integrate AVIF:
While AVIF is an exciting advancement in image compression, it is essential to note that AVIF is not yet universally supported by all web browsers.
As a result, it may be beneficial to focus on utilizing WebP for broader compatibility with current browsers while keeping an eye on AVIF’s development and adoption.
Implement Responsive Design:
As you optimize your images for WebP, take the opportunity to implement responsive design principles.
Create multiple versions of your photos to serve the most appropriate size based on the user’s device and screen resolution, further enhancing the user experience.
Test and Monitor:
After implementing the new image formats, it is crucial to conduct thorough testing to ensure that the changes have not introduced any issues.
Monitor the website’s performance metrics to measure any improvements in load times and user experience.
How to use AVIF and WebP in WordPress
You can Install a WordPress Plugin,supporting AVIF and WebP formats.
One popular option is the “ShortPixel Image Optimizer” plugin, which automatically converts images to WebP/AVIF format.
On my website mssaro , I use this ShortPixel plug-in to convert my pictures into WebP image format.
I did the below setting.
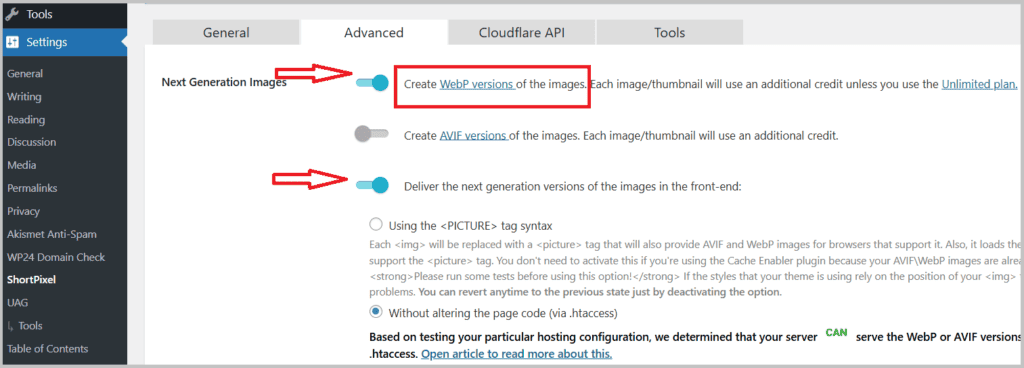
Enable AVIF and WebP Conversion:
Look for options to enable AVIF and WebP conversion within the plugin settings.
I am currently using WebP format.
Optimize Media Library:
Once AVIF and WebP conversion are enabled, you can optimize your existing media library by converting images to these formats. This will help improve your site’s performance and load times.
Update Image Settings:
As you add new images to your WordPress site, ensure they are saved in a format supporting AVIF and WebP. Check the plugin settings to ensure new images are automatically converted to these formats.
Test Performance:
After implementing AVIF and WebP support, test your site’s performance using tools like GTmetrix, PageSpeed Insights, or SEO Site Checkup. You should see improvements in loading times and overall site speed.
Following these steps, you can effectively use WordPress’s AVIF and WebP image formats to enhance your site’s performance and user experience.
How do You Generate WebP and AVIF file formats?
Here are a few methods for generating WebP and AVIF files:
Image editing software:
You can use image editing software such as Adobe Photoshop, GIMP or any other software that supports WebP and AVIF file formats.
Open your image in the software and export/save the file in the desired format.
Using online converters:
Many online image converters allow you to convert images to different formats.
You can upload your image to one of these converters and select WebP or AVIF as the output format.
Browser Extensions:
You can use various tools that are specifically designed for this purpose, like
- Squoosh: Squoosh is a powerful image optimization tool developed by Google. It allows you to convert images to various formats, including WebP and AVIF.
- WebP Loader: WebP Loader is a browser extension that automatically converts images to WebP format when you visit websites.
- AVIFox: It is a browser extension that adds support for AVIF format in the Firefox browser. It allows you to view and download AVIF images on the web. However, please note that AVIFox is currently in beta. It does not support all the features of AVIF.
WebP Converter for Media plugin (WordPress):
By installing the plugin, your existing images will be converted to WebP and AVIF formats without additional steps.
ShortPixel Image Optimizer plugin (WordPress): The ShortPixel Image Optimizer plugin is known for creating AVIF images as an option for image optimization.
Final Takeaway:
Both WebP & AVIF file formats are excellent.
But the question comes, what we should use currently?
AVIF offers better compression than WebP, even in smaller file sizes. However, AVIF is only supported by some popular browsers and may require additional Javascript.
WebP has better browser support than AVIF.
I am using WebP on my site. But in the future, if AVIF improves it’s browser compatibility I would try to move on that.
But one thing surely we can do, convert your existing JPEG, PNG, etc, format into webP at least for better website performance.
What Next You Can Read?
Learn more about ShortPixel Image Optimizer.
Upgrade your knowledge about the best websites that provide free images and pictures.
Keep Smiling, and Start Sharing!
Frequent Ask Questions(FAQ) on AVIF v/s WebP
Answer: AVIF and WEBP are newer image file formats designed to improve compression and reduce image file sizes compared to older formats like JPEG and PNG. AVIF uses the AV1 video codec to compress images, which the Alliance for Open Media developed. Google developed WebP, which uses both lossy and lossless compression algorithms.
Answer: AVIF currently has limited browser support and works only in Chrome, Edge, and Opera. WebP has wider Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Android browsers, and Samsung Internet support. WebP is also supported on many devices, while AVIF support is still patchy.
Answer: The main benefits are smaller file sizes, faster page loads, and bandwidth savings. AVIF and webP support higher color depths, transparency, and animation over JPEG or PNG. Additionally, they achieve better compression with less quality loss than JPEG.
Answer: AVIF and webp can achieve near-lossless image quality at high-quality settings, almost matching PNG. However, in lower-quality settings, some loss of quality and artifacts can be seen compared to PNG or uncompressed images. Overall, AVIF and webp provide good visual quality and improvements over JPEG.
Answer: Implementing new image formats requires configuring server MIME types, using HTML image tags with type attributes, and generating optimized images. However, most modern web development workflows have plugins or libraries to handle new formats easily.
Answer: Best practices include:
1. Generating multiple sizes for responsive breakpoints.
2. Using the picture tag to serve appropriate image sizes.
3. Specifying width/height attributes for page layout.
4. Using modern image CDNs to optimize delivery.
5. Falling back to JPEG/PNG for unsupported browsers.
Answer: Smaller image sizes reduce bandwidth usage and provide faster download times. This results in lower data costs for users and quicker page loads. AVIF/webp allows for serving higher quality images while keeping page weight low.
Answer: Given its superior compression capabilities, AVIF can potentially replace JPEG. However, broad browser support is still needed. WebP serves as an excellent intermediate format, providing better compression than JPEG. The web technology landscape keeps evolving, so new image formats will continue to emerge. But WebP and, eventually, AVIF appear poised to become the next standard.





